8 Facts about Nitrogen in Plant Nutrition
There are 15 elements essential for plant life, 3 of which (oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen) come from the air and water and are generally not taken into account in the area of plant nutrition. Of the remainder nitrogen is considered to be the most important.
78% of the Atmosphere is Nitrogen but its not Usable by Plants
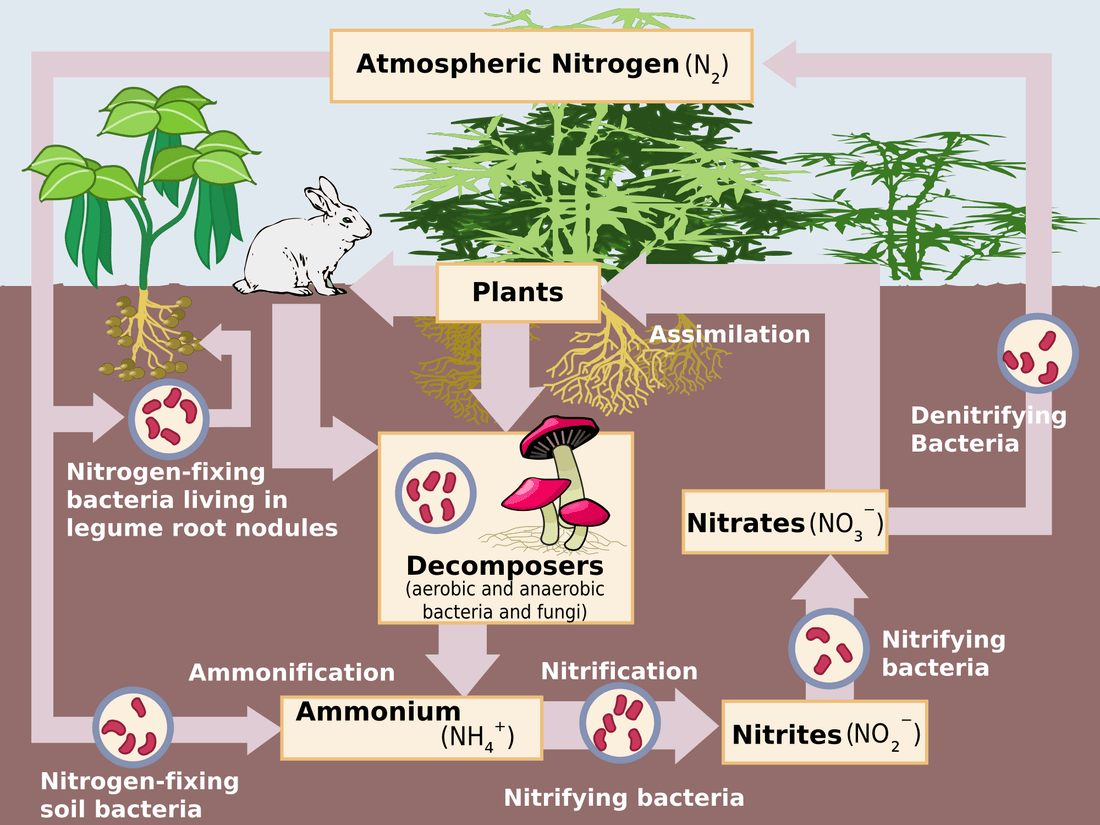
The nitrogen contained in the air is in the N2 form and this molecule is extremely stable, taking a lot of energy to break apart. Plants on the other hand need to have nutrients available as salts in order to absorb and utilize them, in this form nitrogen is referred to as "fixed".
Nitrogen can be Fixed with Lightning
The energy released in the atmosphere causes nitrogen to react with oxygen forming nitrous oxide and nitrogen dioxide. These are unstable and react with water vapour to form nitrous and nitric acids. These are fall to the earth with precipitation, and are then used by plants. The amount is significant at 140,000 tons per year globally.

World War I was Responsible for Modern Fertilizers
Munitions and explosives use nitrogen in their composition and prior to this time most of the worlds nitrogen came from sodium nitrate mined in Chile. This supply was controlled by Great Britain and Germany was cut off from this supply upon the onset of war. German chemists Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch invented a process upon taking hydrogen and nitrogen under high temperature and pressure ammonia would be formed. Once fixed as ammonia it was relatively easy to convert the nitrogen into explosives like nitroglycerin or trinitrotoluene (TNT). For their work, Haber and Bosch received the Nobel Prize in 1931. Their method is used to this day for nitrogen fertilizer as ammonia can be changed into fertilizers like urea, ammonium nitrate etc.
In Nature Most Nitrogen is Fixed by Bacteria
Soil bacteria are responsible for most of the nitrogen being converted from the atmospheric form into usable forms. The enzymes involved in this process are very susceptible to degradation by oxygen and so an anaerobic environment is essential for the growth of these bacteria. There are many species which live freely in the soil but also others that live symbiotically with plants. Plants provide energy to the bacteria in exchange for fixed nitrogen. The most notable of these relationships is between legumes (peas, beans, alfalfa etc) and bacteria in the Rhizobium genus. The plants form nodules in the roots for the bacteria to inhabit and even produce an protein to scrub the nodules of oxygen.

*Did You Know?*
Cyanobacteria (Blue - Green Algae) are able to fix their own nitrogen as well as produce their own energy through photosynthesis. Since they are able to quickly grow with minimum amounts of input, their cultivation has huge potential in the future both as a food source and as an alternative energy form.
Most Nitrogen Fertilizer is in the form of Urea
Once nitrogen is fixed as ammonia through the Haber process, it can be reacted with carbon dioxide to form urea. It has many advantages in that it's relatively high in nitrogen at 46%. It's also relatively safe, ammonium nitrate being potentially explosive together with a combustible. Plants can not use urea very well and it has to converted to ammonia by soil bacteria before its usable by plants. Unfortunately some of the ammonia is lost to the atmosphere before the plants can use it.
Nitrogen is Converted into Proteins and other Biologically Active Compounds
Once a nitrogen salt is absorbed into the plant it will be converted into an amino acid. These are connected together as into long chains and folded into proteins which form a wide variety of metabolic functions. The other notable compounds are nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) as well as some of the secondary metabolites such as alkaloids, amines, cyanogenic glycosides and glucosinolates.

Nitrogens Dark Side
While nitrogen fertilizer has been a huge contributor to having a stable food supply using it has some detrimental effects on the environment. The Haber process uses high temperatures and pressures which uses natural gas as an energy source. This contributes significantly to climate change.
Not all fertilizer is used by plants and can be washed out of the soil with precipitation. This winds up in lakes and rivers and can cause algae blooms. In turn the blooms use up the oxygen from the water killing fish.

There are Different Forms of Nitrogen
In addition to urea which was discussed previously there are 3 other forms to be aware of in plant nutrition. Nitrate (NO3), being the form which the plant prefers and is found in such fertilizers as potassium, calcium and magnesium nitrates. The ammonical (NH4) is also easily usable by the plant but is converted to nitrate in the roots before being transported throughout the plant. Fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate and phosphate being the most common forms. The third form is organic nitrogen, typically its in the form of proteins and has to be broken down in the soil before the plant can use it. Fertilizers in this form are generally a lot lower in nitrogen that synthetic forms, examples being blood and feather meals.
