Cannabis Growing Glossary
- 420
- 710
- 2-AG
- 510 Thread
- 12/12 Lighting Schedule
- 60/40 Sativa-Indica Ratio
- 6/2 Lighting Schedule
- 24/0 Lighting Schedule
- 10-20 Rule
- 3-Part Nutrients
- 2-Part Nutrients
- 1-Part Nutrients
- 16/8 Lighting Schedule
- 50/50 Hybrid
- Aeroponics
- Autoflowering
- Amendments
- Anatomy
- Apical Dominance
- Aquaponics
- Auxins
- Alkalinity
- Air Pruning
- Bud
- Bloom Phase
- Botrytis
- Beneficial Insects
- Biomass
- Buffering
- Brix
- Broad Spectrum
- Bract
- Calyx
- Cloning
- Cannabinoids
- CO2 Enrichment
- Curing
- Cotyledon
- Companion Planting
- Crossbreeding
- Cannabis Ruderalis
- Chlorophyll
- Decarboxylation
- Dioecious
- Drip Irrigation
- Detoxification
- Damping-off
- Dark Period
- Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Dispensary
- Drainage
- Dry Sift
- EC (Electrical Conductivity)
- Edibles
- Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
- Entourage Effect
- Ebb and Flow
- Ethanol Extraction
- Evapotranspiration
- Enzymes
- Early Flowering
- Etiolation
- Feminized Seeds
- Flowering Stage
- Foliar Feeding
- Flush
- Full Spectrum LED Lights
- Fan Leaves
- Fungicides
- FIMming
- Fertigation
- Feminization
- Germination
- Genotype
- Grafting
- Grow Medium
- Gibberellins
- Ganja
- Greenhouse Growing
- Guerrilla Growing
- Guttation
- Genetic Drift
- Hydroponics
- Humidity
- Hermaphrodite
- Heirloom
- HPS (High-Pressure Sodium) Lights
- Hybrid
- Hashish (Hash)
- Horticulture
- Humic Acids
- Hybrid Vigor (Heterosis)
- Indica
- Irrigation
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Internode
- Inoculation
- Indoor Growing
- Insecticidal Soap
- Indole-3-butyric Acid (IBA)
- Ionic Nutrients
- Isolation
- Joint
- Jiffy Pots
- Juicing
- Jeweler’s Loupe
- Jute
- Jarring
- Jack Herer
- Kush
- Kelvin Scale
- Kief
- Knuckle
- Kelp Extract
- Kratky
- Landrace
- LED (Light Emitting Diode)
- Lollipopping
- Leaching
- Live Resin
- Limonene
- Loam
- Leggy
- LST (Low-Stress Training)
- Leaf Septoria
- Mother Plant
- Micronutrients
- Mycorrhizae
- Macronutrients
- Mulch
- Mainlining
- Marijuana
- Medium
- Mold
- Manicuring
- Node
- Nutrients
- Necrosis
- Nitrogen
- NFT (Nutrient Film Technique)
- Neem Oil
- Nug
- N-P-K Ratio
- Netting
- Non-Polar Solvent
- Organic
- Overwatering
- Oxidation
- Osmosis
- Odor Control
- Open Pollination
- Outcross
- OG
- Ounce
- Offset
- Photosynthesis
- pH Level
- Photoperiod
- Propagation
- Pistil
- Pest Management
- Perlite
- Potassium (K)
- Pollen
- Phenotype
- Phosphorus (P)
- Quarter
- Querkle
- Quick-Drying
- Quantum Board LED Grow Lights
- Quality Control
- Quartz
- QP
- Quercetin
- Quick Cure
- Root Bound
- Rhizosphere
- Rosin
- Rockwool
- Resin
- Regeneration
- Ripening
- Root Pruning
- Re-vegging
- Strain
- Sativa
- Screen of Green (SCROG)
- Substrate
- Sinsemilla
- Stomata
- Supercropping
- SOG (Sea of Green)
- Solventless Extraction
- Stigma
- Sclerotinia
- Stress Training
- Terpenes
- Topping
- Trichomes
- Transplanting
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
- Tincture
- Trellising
- Tillering
- Thermoperiodicity
- Trimming
- UV Light
- Uptake
- Undercutting
- Unisex
- Uniformity
- Up-Potting
- Urban Gardening
- Umbrella Training
- Undercutting
- Unisex
- Vegetative Stage
- Ventilation
- Vermiculite
- Vertical Growing
- Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD)
- Volatilization
- Viability
- Virus
- Vascular System
- Variegation
- Watering Schedule
- Wattage
- Wicking
- Weeding
- Wet Trimming
- Windburn
- White Label
- Worm Castings
- Whole Plant Extract
- Wilting
- Xanthophyll
- Xeriscaping
- Xylem
- Xerophyte
- X-Factor
- Yellowing
- Yield
- Yucca
- Yumbolt
- Zeolite
- Zinc (Zn)
- Zonal Germination
- Zymurgy
#
- 420
- 710
- 2-AG
- 510 Thread
- 12/12 Lighting Schedule
- 60/40 Sativa-Indica Ratio
- 6/2 Lighting Schedule
- 24/0 Lighting Schedule
- 10-20 Rule
- 3-Part Nutrients
- 2-Part Nutrients
- 1-Part Nutrients
- 16/8 Lighting Schedule
- 50/50 Hybrid
420
The term "420" has become one of the most widely recognized codes in cannabis culture, symbolizing a time to consume cannabis (4:20 PM) as well as a day for celebration and advocacy (April 20th). It's a day when enthusiasts gather to celebrate the progress of cannabis reform and reflect on the work still needed to de-stigmatize and legalize the plant.
Today, "420" not only marks a time and date to enjoy cannabis but also serves as a rallying point for political activism, social gatherings, and a call for the normalization and legalization of cannabis.
710
A number used to refer to cannabis oils and concentrates. When flipped upside down, "710" spells "OIL," and July 10th has become a day to celebrate and consume cannabis concentrates.
2-AG
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is an endocannabinoid, a naturally occurring cannabinoid within the human body that interacts with the endocannabinoid system, similarly to how plant cannabinoids like THC and CBD do.
510 Thread
A type of threading used on vape pens and cartridges. The "510" refers to the threading pattern: 10 threads at 0.5mm each. It's become a standard in the industry, making many cartridges and batteries interchangeable.
12/12 Lighting Schedule
A lighting schedule used to induce flowering in photoperiod cannabis plants. The plants are given 12 hours of light followed by 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness each day, mimicking the natural transition from summer to fall.
60/40 Sativa-Indica Ratio
This ratio describes the genetic makeup of a hybrid cannabis strain. It indicates that the strain is composed of 60% Sativa genetics and 40% Indica genetics, affecting its growth characteristics and effects.
6/2 Lighting Schedule
An alternative lighting schedule for vegetative growth where plants receive light in blocks of 6 hours followed by 2 hours of darkness. Some growers believe this schedule may improve growth rates over a continuous 24-hour light cycle.
24/0 Lighting Schedule
A lighting schedule where plants are exposed to light 24 hours a day, which can be used during the vegetative stage to maximize growth. However, some growers prefer a short dark period for plant rest.
10-20 Rule
This rule is a guideline for germinating seeds, suggesting that the ideal temperature range for seed germination is between 10°C and 20°C.
3-Part Nutrients
A three-part nutrient system splits essential plant nutrients across three separate solutions, allowing growers to adjust and administer specific nutrient types at different stages of plant growth. This typically includes a formula for vegetative growth, another for overall plant health and micronutrients, and a third for the flowering stage. This customizable approach caters to the changing needs of the plant from seedling to harvest.
2-Part Nutrients
A two-part nutrient system simplifies plant feeding by splitting essential nutrients into two solutions, commonly referred to as "Part A" and "Part B." Part A typically contains certain macro and micro-nutrients, while Part B complements with the rest, ensuring plants receive a comprehensive, balanced diet throughout their lifecycle. This system streamlines the mixing process and is ideal for growers looking for efficiency without sacrificing plant health or yield.
1-Part Nutrients
One-part nutrients provide a complete, balanced blend of essential macro and micronutrients in a single solution, offering the ultimate simplicity for feeding cannabis plants. This straightforward system is perfect for novice growers or those who prefer an uncomplicated approach to plant nutrition.
16/8 Lighting Schedule
A common light cycle used in the vegetative stage of cannabis growth, where plants receive 16 hours of light and 8 hours of darkness. This mimics the long days of summer and promotes vigorous vegetative growth.
50/50 Hybrid
A cannabis strain that is an even split between indica and sativa genetics, potentially offering a balance between the typical effects of each variety.
A
- Aeroponics
- Autoflowering
- Amendments
- Anatomy
- Apical Dominance
- Aquaponics
- Auxins
- Alkalinity
- Air Pruning
Aeroponics
Aeroponics is an advanced cultivation method where plants are grown in an air or mist environment without the use of soil or an aggregate medium. The roots hang in the air and are periodically misted with a nutrient-rich solution, allowing for maximum oxygen uptake and nutrient efficiency. This method is known for promoting rapid growth rates, higher yields, and reducing the risk of soil-borne pests and diseases.
Autoflowering
Autoflowering cannabis strains are genetically designed to flower automatically after a certain period of growth, typically 2-4 weeks, regardless of light cycle changes. These strains are particularly appealing for their simplicity and speed, as they allow for multiple harvests within a single season and are generally less demanding in terms of lighting management.
Amendments
Soil or growing medium amendments are materials added to improve the medium's physical properties, nutrient balance, and water retention capabilities. Organic amendments include compost, manure, and bone meal, which slowly enrich the soil with nutrients. Inorganic amendments, such as perlite and vermiculite, improve aeration and drainage.
Anatomy
Key components include the roots, responsible for nutrient and water uptake; the stem, which supports the plant; leaves, the site of photosynthesis; and flowers, where cannabinoids and terpenes are produced. Familiarity with each part helps in diagnosing health issues and optimizing growth.
Apical Dominance
Apical dominance is a growth pattern where the main stem of the cannabis plant grows more vigorously than the side branches, leading to a taller, less bushy plant. Growers often manipulate this natural tendency through techniques like topping (cutting off the plant's top) or FIMming (pinching the top leaves), encouraging a more lateral growth to increase light exposure and yield.
Aquaponics
Aquaponics combines fish farming (aquaculture) with soilless plant cultivation (hydroponics) in a closed-loop system. Fish waste provides organic nutrients for the plants, while the plants clean and filter the water, which is recirculated back to the fish tanks. This sustainable method mimics natural ecosystems, making it efficient and environmentally friendly.
Auxins
Auxins are a group of plant hormones crucial for growth and development, influencing cell elongation, bud formation, and root development. They play a significant role in shaping the plant's architecture, including the suppression of lateral branch growth in favor of the main stem, known as apical dominance.
Alkalinity
Alkalinity in the context of cannabis cultivation refers to the water or growing medium's capacity to neutralize acids, which is crucial for maintaining a stable pH level. A proper pH level ensures that plants can effectively absorb nutrients. Most cannabis plants thrive in slightly acidic conditions (pH 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics, 6.0-7.0 for soil).
Air Pruning
Air pruning is a technique used in container gardening to encourage a healthier root system. When roots reach the edge of a breathable fabric pot, the exposed air naturally prunes them, preventing circling and promoting the growth of new feeder roots. This results in a more fibrous root structure, enhancing the plant's ability to uptake water and nutrients, leading to improved overall health and growth.
B
- Bud
- Bloom Phase
- Botrytis
- Beneficial Insects
- Biomass
- Buffering
- Brix
- Broad Spectrum
- Bract
Bud
The bud refers to the flower of the cannabis plant, which is the primary site for cannabinoid and terpene production, making it the most valuable part of the plant for medicinal and recreational use. Buds are harvested, dried, and cured before consumption. They are characterized by their dense, resinous structure, rich in trichomes.
Bloom Phase
The bloom phase, or flowering stage, is when cannabis plants develop their buds. This stage is triggered by changing the light cycle to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. During this period, plants require different nutrients, primarily phosphorus and potassium, to support bud formation and development.
Botrytis
Also known as bud rot or gray mold, Botrytis is a common fungal disease that affects cannabis plants, especially during the flowering stage under high humidity conditions. It can devastate crops by rotting the buds from the inside out. Prevention involves maintaining optimal airflow, humidity, and plant health.
Beneficial Insects
A ballast is an electrical device used with HID (high-intensity discharge) lamps, such as metal halide or high-pressure sodium lights, to regulate the voltage and current supplied to the lamp. Ensuring stable operation and extending the lamp's lifespan. Digital ballasts are preferred for their efficiency and ability to adjust output levels.
Biomass
In cannabis cultivation, biomass refers to the total mass of organic material (plants or parts of plants) produced in a given area or volume. It can include both usable material, such as buds and leaves, and waste material. Biomass is often measured to evaluate yield efficiency and can be used for extraction purposes.
Buffering
Buffering refers to the process of pre-treating growing mediums (like coco coir) with calcium and magnesium to stabilize pH levels and nutrient availability. This ensures that the medium will not leach essential nutrients from the solution or plants, promoting healthier growth and development.
Brix
Brix is a measure of the sugar content in an aqueous solution and, by extension, in plant sap. In cannabis cultivation, a higher Brix level indicates a healthier plant that is more resistant to pests and diseases, as well as potentially more flavorful and potent buds due to increased nutrient density.
Broad Spectrum
Broad-spectrum lighting refers to artificial light sources that emit a wide range of wavelengths, simulating the natural sunlight spectrum. This is beneficial for cannabis growth, as different wavelengths are utilized during various growth stages, from vegetative growth to flowering.
Bract
A bract is a leaf-like structure that encases the female cannabis flower's reproductive parts. Bracts are densely coated with resin glands (trichomes) that produce high concentrations of cannabinoids and terpenes. The size and number of bracts can be an indicator of a flower's potency.
C
- Calyx
- Cloning
- Cannabinoids
- CO2 Enrichment
- Curing
- Cotyledon
- Companion Planting
- Crossbreeding
- Cannabis Ruderalis
- Chlorophyll
Calyx
The calyx is the protective floral structure of female cannabis plants, consisting of small, leaf-like parts that form the outer layer of the buds. It houses the reproductive organs and is where the majority of the plant’s cannabinoids and terpenes are produced. During flowering, the calyces swell and can give clues about the plant's readiness for harvest.
Cloning
Cloning involves taking cuttings from a mature cannabis plant to create genetically identical offshoots. This technique allows growers to replicate plants with desirable traits, such as potency, aroma, or yield, without starting from seeds. Clones skip the seed germination stage, providing a uniform crop that mirrors the parent plant’s characteristics.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in cannabis that interact with the human body's endocannabinoid system, producing various effects. The most well-known cannabinoids are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), responsible for the plant's psychoactive effects, and CBD (cannabidiol), known for its therapeutic benefits without inducing a high. Other cannabinoids include CBG, CBN, and THCV, each with unique properties and potential health benefits.
CO2 Enrichment
CO2 enrichment is a technique used in indoor growing to increase carbon dioxide levels in the air, enhancing photosynthesis and plant growth. Since CO2 is a critical component for photosynthesis, higher concentrations can lead to faster growth rates and potentially higher yields. However, this technique requires careful monitoring and control systems to maintain optimal levels and ensure plant health.
Curing
Curing is the process of slowly drying harvested cannabis buds in controlled conditions to enhance their flavor, aroma, and potency. Proper curing removes moisture from the buds, preventing mold and bacterial growth while allowing for the gradual breakdown of chlorophyll and the maturation of cannabinoids and terpenes. The result is a smoother, more pleasant smoking or vaping experience.
Cotyledon
Cotyledon refers to the first set of leaves that emerge from a cannabis seedling. These are not true leaves but rather part of the seed's embryo. Cotyledons play a crucial role in the early life of the plant, providing nutrients until the plant can perform photosynthesis with its true leaves. They are typically broader and differ in shape from the plant’s subsequent leaves.
Companion Planting
Companion planting is a cultivation practice that involves growing cannabis alongside other plants to benefit from natural synergies, such as pest control, improved soil health, and enhanced growth. Examples include planting basil to repel insects, marigolds to deter nematodes, and clover to fix nitrogen in the soil. This method promotes a biodiverse ecosystem that supports healthier plants.
Crossbreeding
Crossbreeding is the process of mating two different cannabis strains to combine desirable traits from both parents, such as disease resistance, yield size, flavor profile, or cannabinoid content. The resulting hybrid strain inherits characteristics from both parent strains, potentially leading to new varieties with unique attributes.
Cannabis Ruderalis
Cannabis ruderalis is a subspecies of the cannabis plant, less known than its sativa and indica counterparts. It is native to areas in Central and Eastern Europe and Russia. Ruderalis plants are small, hardy, and have an autoflowering trait, meaning they flower based on age rather than light cycles. This trait has been harnessed to create autoflowering hybrid strains.
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the leaves and stems of cannabis plants, crucial for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light into chemical energy. While chlorophyll is vital for growth, its presence in large quantities can affect the smoothness and flavor of smoked cannabis. Proper curing reduces chlorophyll in the buds, improving taste and reducing harshness.
D
- Decarboxylation
- Dioecious
- Drip Irrigation
- Detoxification
- Damping-off
- Dark Period
- Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Dispensary
- Drainage
- Dry Sift
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical process that activates the psychoactive and therapeutic compounds in cannabis. By applying heat, the process converts THCA and CBDA, the non-active acid forms of THC and CBD found in the raw plant, into their active forms, THC and CBD. This process is crucial for making cannabis-infused edibles, tinctures, and oils effective.
Dioecious
Cannabis is typically dioecious, meaning it has separate male and female plants. Female plants produce the resinous buds sought after by consumers and growers, while male plants produce pollen for reproduction. For most growers, especially those cultivating for flower production, identifying and removing male plants early in the growing cycle is important to prevent pollination, which leads to seeded buds.
Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a water-efficient irrigation method that delivers water directly to the base of each plant through a network of tubing and emitters. This system minimizes water waste and evaporation by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, providing a controlled and precise water supply. It's especially beneficial in areas with water scarcity or for growers looking to reduce their water footprint.
Detoxification
In the context of cannabis, detoxification refers to the process of eliminating traces of cannabinoids from the body, commonly undertaken by individuals facing drug tests or wishing to take a tolerance break. Detox methods vary in effectiveness and can include hydration, exercise, and the use of detoxification products.
Damping-off
Damping-off is a term used to describe a variety of diseases that affect seedlings, causing them to rot at the stem base, wilt, and collapse. This condition is typically caused by fungal pathogens in the soil or growing medium, especially in conditions of high humidity and poor ventilation. Preventative measures include using sterile soil, proper spacing, and adequate airflow.
Dark Period
The dark period refers to the uninterrupted night phase required by cannabis plants, especially during the flowering stage. Cannabis plants are photoperiod sensitive, meaning their flowering cycle is triggered by changes in the light/dark cycle. Maintaining a consistent and uninterrupted dark period is crucial for inducing and sustaining the flowering phase in photoperiod strains.
Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, commonly known as THC, is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis that produces the "high" associated with marijuana use. THC interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, affecting mood, perception, and cognition. Its potency and effects can vary significantly among different cannabis strains.
Dispensary
A dispensary is a legal retail outlet where cannabis products are sold to consumers. Dispensaries can vary widely in terms of the products they offer, including various strains of flower, edibles, concentrates, tinctures, and topicals. Staff at dispensaries often provide guidance to consumers to help them select products that meet their needs and preferences.
Drainage
Proper drainage is essential in cannabis cultivation to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other moisture-related issues. Whether growing in soil or a hydroponic system, ensuring that excess water can escape from the root zone is critical for maintaining healthy plant growth and preventing nutrient imbalances.
Dry Sift
Dry sift refers to a solventless extraction method that separates trichomes (the resin glands containing cannabinoids and terpenes) from the rest of the cannabis plant material using a series of screens. The resulting product is a fine, kief-like powder that can be used as is or further processed into hash. Dry sifting is valued for preserving the natural flavors and qualities of the cannabis.
E
- EC (Electrical Conductivity)
- Edibles
- Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
- Entourage Effect
- Ebb and Flow
- Ethanol Extraction
- Evapotranspiration
- Enzymes
- Early Flowering
- Etiolation
EC (Electrical Conductivity)
EC measures the electrical conductivity in a solution, which correlates to the concentration of soluble salts, or nutrients, present. In cannabis cultivation, monitoring EC levels is crucial for understanding the nutrient strength of a solution being fed to plants. Optimal EC levels ensure that plants receive the right amount of nutrients, neither too much (which can lead to nutrient burn) nor too little (leading to deficiencies).
Edibles
Edibles refer to food products infused with cannabis extracts or concentrates. They offer an alternative to smoking or vaporizing, providing effects that typically last longer and can be more intense. The onset time of edibles is slower, as THC is processed by the liver into 11-hydroxy-THC, a potent form of THC. Edibles' potency and delayed effects necessitate careful dosage management.
Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
The endocannabinoid system is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring THC. Present in all mammals, the ECS plays a role in regulating a range of functions and processes, including sleep, mood, appetite, memory, and reproduction. Cannabinoids from cannabis, such as THC and CBD, interact with the ECS, influencing its activities and potentially offering therapeutic benefits.
Entourage Effect
The entourage effect is a theory that suggests the various compounds in cannabis, including cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, work together synergistically to produce a more significant effect than any single compound alone. This concept supports the use of whole-plant extracts over isolated compounds, as the full spectrum of cannabis' components may offer enhanced therapeutic benefits.
Ebb and Flow
Ebb and Flow, also known as flood and drain, is a type of hydroponic system where plants are grown in a tray that periodically floods with nutrient solution before draining back into a reservoir. This method ensures that roots receive ample nutrients and oxygen. Ebb and Flow systems are favored for their simplicity, efficiency, and effectiveness in promoting robust plant growth.
Ethanol Extraction
Ethanol extraction is a common method used to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from the cannabis plant for use in oils, tinctures, edibles, and other products. Ethanol is a solvent that efficiently extracts a wide range of compounds, making it versatile for producing full-spectrum extracts. However, the process must be carefully managed to ensure the removal of all residual solvent from the final product.
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration combines two processes: evaporation of water from soil and transpiration from plants. This process is critical in understanding the water needs of cannabis plants, as it influences irrigation practices. Monitoring evapotranspiration rates helps growers optimize water use, ensuring plants receive sufficient hydration without overwatering, thus promoting healthy growth and development.
Enzymes
In cannabis cultivation, enzymes play vital roles in plant growth and soil health. They catalyze essential biochemical reactions in the plant, facilitating nutrient uptake, photosynthesis, and defense against pathogens. In soil, enzymes help break down organic matter into nutrients that plants can absorb, enhancing soil fertility and plant health.
Early Flowering
Early flowering refers to the phase when cannabis plants begin to develop buds or flowers. This stage is critical for growers to monitor, as it signifies the transition from vegetative growth to the reproductive phase. Environmental factors, especially light cycles, trigger this stage in photoperiod plants, while autoflowering strains transition based on age.
Etiolation
Etiolation occurs when a cannabis plant grows with insufficient light, leading to stretched, weak, and pale growth as it reaches for a light source. This condition highlights the importance of proper lighting in cannabis cultivation. Etiolated plants often have reduced yields and potency, emphasizing the need for adequate and appropriate light exposure throughout the growth cycle.
F
- Feminized Seeds
- Flowering Stage
- Foliar Feeding
- Flush
- Full Spectrum LED Lights
- Fan Leaves
- Fungicides
- FIMming
- Fertigation
- Feminization
Feminized Seeds
Feminized seeds are bred to contain no male chromosomes, ensuring that every plant grown from these seeds will flower as a female. Female cannabis plants produce the buds that are harvested for medical and recreational use. Using feminized seeds simplifies the growing process by eliminating the need to identify and remove male plants, which do not produce consumable flowers and can pollinate females, leading to seeded flowers.
Flowering Stage
The flowering stage is the period in the cannabis plant's life cycle when it develops buds. This stage follows the vegetative growth phase and is triggered by changes in the light cycle—typically, a switch from long days to shorter days. Indoor growers can initiate flowering by adjusting their lighting schedule to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. This stage requires careful attention to nutrient, water, and light needs to maximize bud development.
Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding is a method of feeding plants by applying liquid fertilizer directly to their leaves instead of the soil. This technique can be an effective way to address nutrient deficiencies quickly, as the leaves can absorb nutrients more rapidly than roots. However, it's typically used as a supplementary feeding method and should be done with care to avoid leaf burn or fungal issues.
Flush
Flushing is a technique used towards the end of the flowering stage, where growers stop administering nutrients and water the plants with plain water instead. This process is believed to remove excess nutrients from the plant's system, potentially improving the taste and quality of the final bud by ensuring that the plant burns cleaner.
Full Spectrum LED Lights
Full spectrum LED lights are designed to mimic natural sunlight, providing a range of light wavelengths that cannabis plants need for photosynthesis and healthy growth throughout all stages of their life cycle. These lights are energy-efficient, produce less heat than traditional grow lights, and are considered ideal for growing high-quality cannabis indoors.
Fan Leaves
Fan leaves are the large, iconic leaves that are synonymous with the cannabis plant. While they don't produce THC themselves, they play a crucial role in photosynthesis, capturing light energy to convert it into chemical energy. Though not potent, fan leaves can still be used to make extracts or edibles.
Fungicides
Fungicides are chemical or natural substances used to kill or inhibit the growth of fungi that can cause diseases in cannabis plants. While effective in protecting plants, their use should be carefully managed, especially in flowering stages, to avoid contaminating the buds and ensuring consumer safety.
FIMming
FIMming (Fuck I Missed) is a plant training technique similar to topping, intended to increase the plant's bushiness and potential yield. By cutting a portion of the main stem, FIMming causes the plant to produce multiple new growing tips. This method is less precise than topping and can result in more varied growth patterns.
Fertigation
Fertigation is the process of delivering nutrients to plants through the irrigation system, combining fertilization and irrigation. This method allows for precise control over the amount and type of nutrients delivered, optimizing plant health and productivity. Fertigation is especially popular in hydroponic setups but can be used in soil-based cultivation as well.
Feminization
Feminization is a process used to produce feminized cannabis seeds. This involves inducing female plants to produce pollen, which is then used to pollinate other female plants. The resulting seeds are genetically female, minimizing the chances of male plants growing and ensuring that nearly all plants will produce buds.
G
- Germination
- Genotype
- Grafting
- Grow Medium
- Gibberellins
- Ganja
- Greenhouse Growing
- Guerrilla Growing
- Guttation
- Genetic Drift
Germination
Germination is the initial stage of a cannabis plant's life cycle, starting when a seed cracks open and sprouts its first root (the radicle) and shoot. Proper germination conditions include moisture, warmth, and darkness. This critical phase sets the foundation for a healthy plant, leading to successful cultivation.
Genotype
The genotype of a cannabis plant refers to its genetic makeup, including all its inherited traits. The genotype determines potential characteristics like growth habit, cannabinoid content, and resistance to pests and diseases. However, the actual expression of these traits (phenotype) can be influenced by environmental conditions.
Grafting
Grafting is a horticultural technique where tissues of plants are joined so they continue their growth together. In cannabis cultivation, grafting can allow a grower to produce multiple strains on a single plant or to combine different plant qualities, such as vigor or pest resistance, onto a chosen stock.
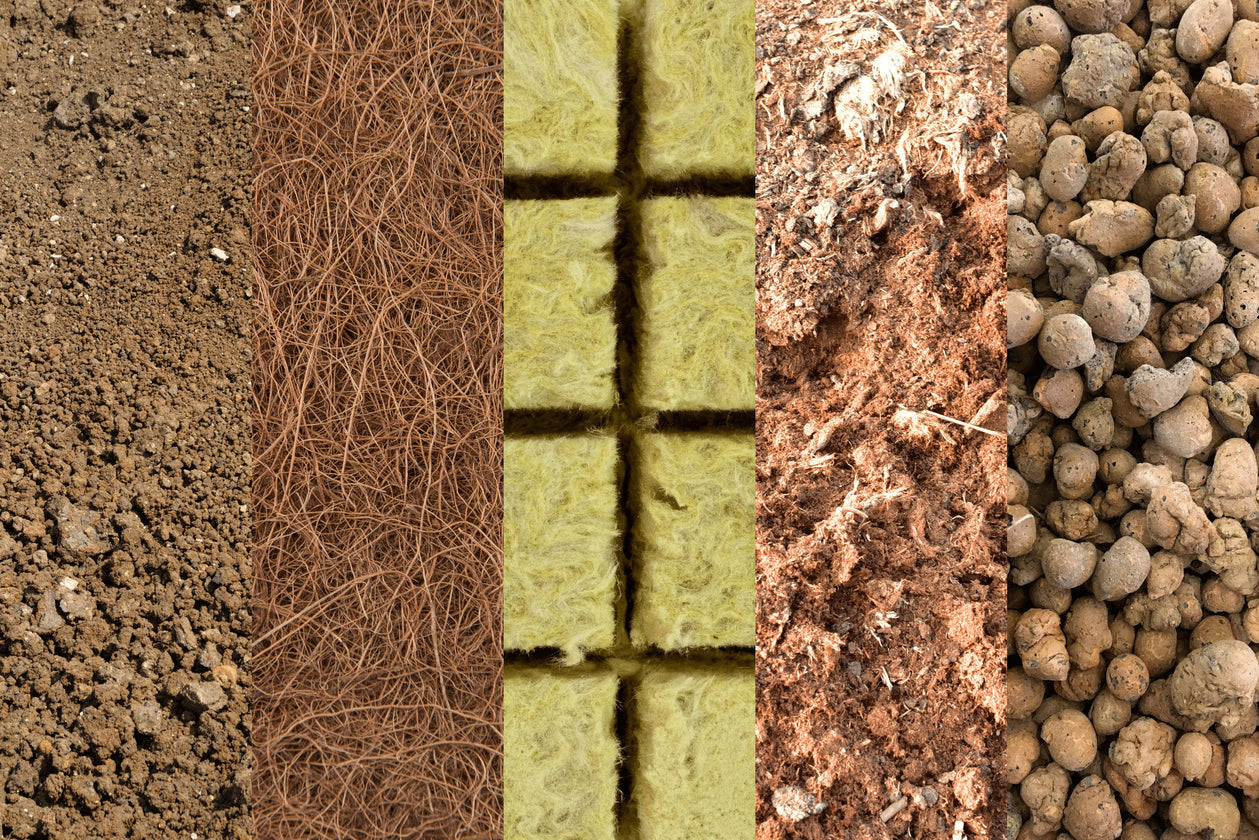
Grow Medium
The grow medium is the material in which the cannabis roots grow. Common mediums include soil, coco coir, hydroponic solutions, and aeroponic mists. The choice of medium can affect water retention, nutrient availability, and the overall health and development of the plant.
Gibberellins
Gibberellins are plant hormones that play a crucial role in various growth processes, including seed germination, stem elongation, and flowering. In cannabis cultivation, manipulating gibberellin levels can influence plant height and the timing of flowering, offering another tool for growers to manage crop development.
Ganja
Ganja is a term of Sanskrit origin, traditionally used in some cultures to refer to the cannabis plant or its flowers. In contemporary usage, it often refers specifically to cannabis buds used for smoking or other forms of consumption.
Greenhouse Growing
Greenhouse growing involves cultivating cannabis plants in a glass or plastic-enclosed structure that offers protection from the elements while taking advantage of natural sunlight. Greenhouses can extend growing seasons, control environmental conditions more efficiently than open-air cultivation, and reduce the need for artificial lighting.
Guerrilla Growing
Guerrilla growing refers to cultivating cannabis in secret, hidden outdoor locations to avoid detection and legal repercussions. This method relies on natural soil and sunlight, with growers typically choosing remote spots that are not easily accessible or visible to passersby.
Guttation
Guttation is the process by which plants exude droplets of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves, often seen in the early morning. While a normal physiological process, excessive guttation can indicate overwatering or poor water management in the cultivation environment.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift in cannabis cultivation refers to the gradual change in the frequency of genetic traits in a population over time, especially in small populations or those reproduced from a limited number of parents. This can lead to a loss of genetic diversity and may impact the stability and characteristics of strains over generations.
H
- Hydroponics
- Humidity
- Hermaphrodite
- Heirloom
- HPS (High-Pressure Sodium) Lights
- Hybrid
- Hashish (Hash)
- Horticulture
- Humic Acids
- Hybrid Vigor (Heterosis)
Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in a water solvent. This allows for more efficient nutrient absorption and faster growth rates. Cannabis cultivated hydroponically often yields more potent and higher-quality buds due to the controlled environment and direct nutrient management.
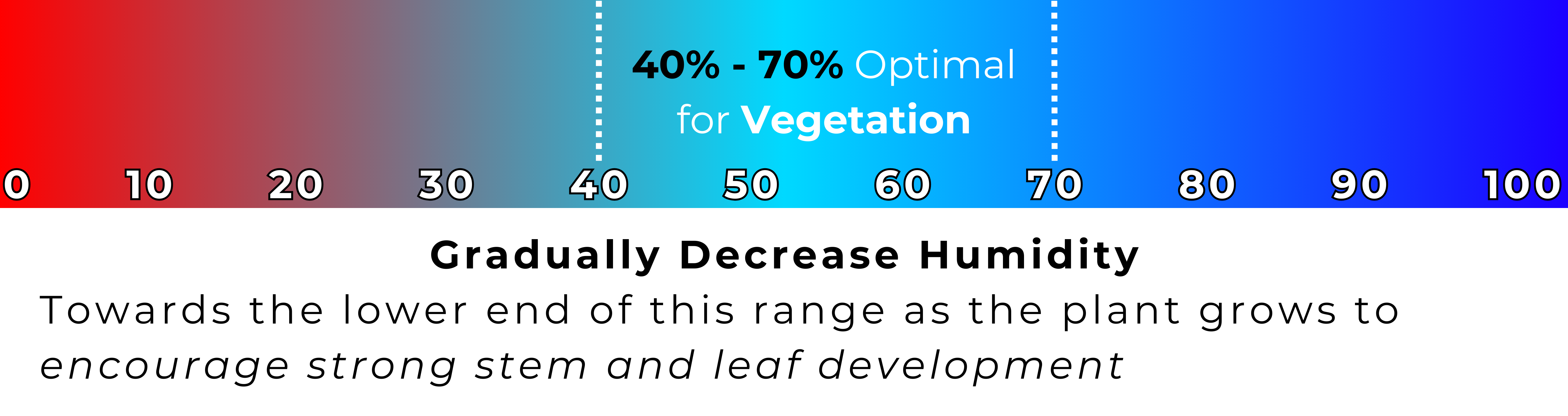
Humidity
Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air. Controlling humidity levels is crucial in cannabis cultivation, as different growth stages require different humidity levels. For example, higher humidity is beneficial during the vegetative stage, while lower humidity helps prevent mold and mildew during flowering.
Hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite cannabis plant possesses both male and female reproductive organs, allowing it to pollinate itself and produce seeds. This can occur due to genetic factors or environmental stress. Hermaphrodites are generally undesirable in cannabis cultivation focused on bud production, as pollination leads to seeded flowers.
Heirloom
Heirloom cannabis strains are pure, traditional varieties that have been passed down through generations, without crossbreeding with other strains. They are valued for their unique genetic properties, offering a diverse range of flavors, aromas, and effects.
HPS (High-Pressure Sodium) Lights
HPS lights are a type of high-intensity discharge (HID) lighting commonly used in cannabis cultivation. They emit a strong, yellow-orange light that is beneficial for the flowering stage, promoting dense bud development. However, they are less energy-efficient than LED lights and generate more heat.
Hybrid
A hybrid cannabis strain is created by crossing two different strains, typically combining traits from both indica and sativa varieties. Hybrids are bred to target specific characteristics, such as flavor, potency, yield, and resilience to pests or diseases.
Hashish (Hash)
Hashish, or hash, is a concentrate made from the compressed or purified preparations of the resin glands (trichomes) of the cannabis plant. It varies in color from light blonde to dark brown and is known for its high potency due to concentrated levels of THC and other cannabinoids.
Horticulture
Horticulture is the art and science of plant cultivation, encompassing the process of breeding, growing, and maintaining plants. In the context of cannabis, horticulture involves selecting suitable strains, optimizing growing conditions, and employing techniques to enhance the quality and yield of the harvest.
Humic Acids
Humic acids are a group of molecules that result from the decay of organic matter, found in humus-rich soil, peat, and coal. In cannabis cultivation, they are used as a soil supplement to improve nutrient uptake, water retention, and root vitality, promoting healthier plant growth.
Hybrid Vigor (Heterosis)
Hybrid vigor refers to the phenomenon where a hybrid offspring exhibits superior qualities or growth characteristics compared to its parents. This can result in more robust plants, higher yields, and greater resistance to pests and diseases. Hybrid vigor is a key concept in breeding new cannabis strains for enhanced traits.
I
- Indica
- Irrigation
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Internode
- Inoculation
- Indoor Growing
- Insecticidal Soap
- Indole-3-butyric Acid (IBA)
- Ionic Nutrients
- Isolation
Indica
Indica refers to one of the primary types of cannabis strains, known for its shorter, bushier plants compared to sativa. Indica strains are often associated with a relaxing, sedative effect, making them popular for evening use. They typically have higher CBD content relative to THC, which contributes to their calming properties.
Irrigation
Irrigation in cannabis cultivation involves the methods and systems used to water plants. Proper irrigation ensures that plants receive the right amount of water at the right time, which is crucial for optimal growth and health. Techniques vary from manual watering to sophisticated automated systems that deliver water directly to the roots via drip or sprinkler systems.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management is a holistic approach to pest control that prioritizes natural and preventative methods over chemicals. IPM strategies include using beneficial insects, proper sanitation, crop rotation, and barriers to manage pests. The goal is to minimize harm to the environment, humans, and beneficial organisms while effectively managing pest populations.
Internode
The internode is the segment of a stem between two nodes (where leaves and branches grow from the stem). The length of internodes can indicate the health and vigor of a plant, as well as the environmental conditions. Short internodes are typically desired in cannabis cultivation as they indicate a bushier plant with potentially more bud sites.
Inoculation
Inoculation in cannabis growing involves introducing beneficial microbes into the soil or grow medium to enhance plant health. These microbes, including mycorrhizal fungi and beneficial bacteria, can improve nutrient uptake, enhance root growth, and help protect plants from pathogens.
Indoor Growing
Indoor growing refers to cultivating cannabis plants inside a controlled environment, such as a grow room or tent. This method allows growers to control all aspects of the environment, including temperature, humidity, light, and CO2 levels, to optimize growth and yield. Indoor growing is popular in regions with unfavorable outdoor growing conditions and for its ability to produce high-quality cannabis year-round.
Read More
Insecticidal Soap
Insecticidal soap is a safe, eco-friendly pesticide used to control soft-bodied pests like aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies on cannabis plants. Made from potassium fatty acids, it works by breaking down the insect's outer layer, causing dehydration and death. It's a preferred choice for organic growers due to its low toxicity and minimal impact on beneficial insects.
Indole-3-butyric Acid (IBA)
Indole-3-butyric Acid is a plant hormone that stimulates root growth in plant cuttings, making it an essential tool for cloning cannabis plants. IBA promotes the formation of new roots, improving the success rate of cloning, a method used to propagate genetically identical plants.
Ionic Nutrients
Ionic nutrients refer to mineral nutrients in a form that plants can immediately absorb. In hydroponic and some soilless growing systems, nutrients are provided in ionic form within a nutrient solution, allowing for precise control over the plant's nutritional intake and optimizing growth and health.
Isolation
In cannabis cultivation, isolation refers to the practice of separating plants to prevent cross-pollination between different strains or to maintain a controlled breeding environment. Isolation is crucial for developing new strains, preserving genetics, and ensuring the quality and purity of seed production.
J
- Joint
- Jiffy Pots
- Juicing
- Jeweler’s Loupe
- Jute
- Jarring
- Jack Herer
Joint
A joint is a rolled cannabis cigarette, typically hand-rolled with rolling papers. It's one of the most common methods for consuming cannabis. The size, shape, and rolling technique can vary, and sometimes tobacco is mixed with cannabis, especially in regions where this mix is culturally traditional.
Jiffy Pots
Jiffy pots are small, biodegradable containers made from compressed peat moss or coconut coir. They are used for germinating seeds or rooting clones. Once the seedlings have established their root systems, the entire jiffy pot can be planted directly into a larger container or the ground, minimizing root disturbance.
Juicing
Juicing involves processing fresh cannabis leaves and sometimes small buds into a liquid form to consume cannabinoids in their acid form, such as THCA and CBDA, which don't produce psychoactive effects. This method is praised for its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, without the high associated with THC.
Jeweler’s Loupe
A jeweler’s loupe is a small, portable magnifying tool used by cannabis growers to inspect the trichomes on the flower buds. Trichome color and clarity are indicators of a plant's maturity and readiness for harvest. Clear to milky or amber trichome colors suggest the optimal time to harvest for peak potency.
Jute
Jute is a natural fiber used to make twine, rope, and other materials. In cannabis cultivation, jute twine is often used for trellising or supporting plants, especially during the flowering stage when the weight of the buds can cause branches to bend or break. Jute is biodegradable, making it an environmentally friendly option for growers.
Jarring
Jarring is the process of curing cannabis by placing dried buds in airtight jars to develop their aroma, flavor, and potency. The method involves periodic "burping" of the jars to release moisture and prevent mold. This controlled environment allows for even curing and moisture distribution within the buds, enhancing the overall quality of the cannabis. Glass jars are preferred for their non-reactive nature.
Jack Herer
While primarily the name of a famous cannabis activist, "Jack Herer" is also a well-known sativa-dominant cannabis strain named in his honor. It's renowned for its uplifting and creative effects, making it popular among recreational and medicinal users. Including it could acknowledge the cultural heritage and influential strains within the cannabis community.
K
- Kush
- Kelvin Scale
- Kief
- Knuckle
- Kelp Extract
- Kratky
Kush
Kush refers to a lineage of cannabis strains originally found in the Hindu Kush mountain range. These strains are typically indica or indica-dominant, known for their potent effects, distinct aroma, and sturdy growth characteristics. Kush varieties are popular among growers and consumers for their relaxing effects and are often associated with flavors ranging from earthy and floral to sweet and spicy.
Kelvin Scale
The Kelvin scale is used to describe the color temperature of light sources, including grow lights for cannabis cultivation. Lights with lower Kelvin values emit a warmer, reddish light, suitable for the flowering stage, while higher Kelvin values produce cooler, bluish light, ideal for vegetative growth. Selecting the appropriate color temperature can significantly impact plant development and yield.
Kief
Kief consists of the trichomes, or resin glands, that collect at the bottom of a container or grinder. Rich in cannabinoids and terpenes, kief is a potent form of cannabis that can be sprinkled over ground flower to enhance potency, pressed into hash, or used in cooking. It's one of the simplest forms of cannabis concentrate to collect and use.
Knuckle
In cannabis cultivation, a "knuckle" refers to the swollen area that forms on a plant's stem after it has been topped or supercropped. This knuckle becomes a strong point of support for the plant, allowing for better nutrient and water flow to the new branches and promoting healthier, more robust growth.
Kelp Extract
Kelp extract is a common organic additive used in cannabis cultivation. Derived from seaweed, it's rich in micronutrients, vitamins, and plant hormones that can stimulate growth, enhance root development, and improve stress resistance. Kelp extracts are often applied as foliar sprays or added to nutrient solutions for their growth-promoting properties.
Kratky
The Kratky method is a passive hydroponic technique where plants are grown in a nutrient-rich solution without the use of air pumps or electricity. This method allows the plant roots to absorb oxygen as the water level drops, making it a simple and low-maintenance way to cultivate cannabis, especially appealing for beginners or growers looking to minimize their system's complexity and energy use.
L
- Landrace
- LED (Light Emitting Diode)
- Lollipopping
- Leaching
- Live Resin
- Limonene
- Loam
- Leggy
- LST (Low-Stress Training)
- Leaf Septoria
Landrace
A landrace is a cannabis strain that has developed naturally in a particular environment and is adapted to the specific geographical and climatic conditions of its native habitat. These strains are often named after their place of origin and have not been crossbred with other strains, making them genetically pure.
LED (Light Emitting Diode)
LED lights are a highly efficient and energy-saving lighting option for cannabis cultivation. They produce less heat and can be designed to emit specific light spectra ideal for different growth stages. LED technology has advanced to provide full-spectrum lighting suitable for the complete life cycle of a cannabis plant.
Lollipopping
Leaching
Leaching in cannabis cultivation refers to the process of running plain water or a mild flushing solution through the growing medium to remove excess salts and nutrient buildup. This is important to prevent nutrient lockout, where plants can no longer absorb nutrients efficiently.
Live Resin
Live resin is a type of cannabis concentrate made from fresh, frozen flowers as opposed to dried and cured buds. The freezing process preserves the terpenes and cannabinoids, resulting in a more flavorful and aromatic final product.
Limonene
Limonene is a prominent terpene found in cannabis and the peel of citrus fruits. It's known for its potent citrus scent and is believed to have mood-lifting properties. Limonene is also thought to have therapeutic benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Loam
Loam is a type of soil that is considered ideal for growing cannabis due to its balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, along with organic matter. Loamy soil provides excellent drainage, nutrient retention, and aeration, creating an optimal environment for root growth.
Leggy
A "leggy" plant is one that has grown excessively tall and thin, usually due to inadequate light. These plants expend more energy on stem growth in an attempt to reach a light source, which can result in a weaker structure and lower yield.
LST (Low-Stress Training)
Low-Stress Training (LST) involves gently bending and tying down cannabis plant branches to control their shape and height. This technique encourages more horizontal growth, allowing for better light exposure and potentially leading to more even canopy development and increased yields.
Leaf Septoria
Leaf septoria, also known as yellow leaf spot, is a fungal condition that affects the foliage of the cannabis plant, causing yellow and brown spots on the leaves. Managing humidity and air circulation, along with removing affected foliage, can help control the spread of this disease.
M
- Mother Plant
- Micronutrients
- Mycorrhizae
- Macronutrients
- Mulch
- Mainlining
- Marijuana
- Medium
- Mold
- Manicuring
Mother Plant
A mother plant is a cannabis plant kept in the vegetative stage that growers use to take clones from. It's selected for its robust health, desirable traits, and genetic stability to ensure a consistent and reliable crop.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are essential elements required by cannabis plants in small quantities, including sulfur, magnesium, and calcium. Though needed in smaller amounts than macronutrients, they are indispensable for the plant's overall health and development, supporting vital functions and contributing to robust growth.
Mycorrhizae
Mycorrhizae are beneficial fungi that form a symbiotic relationship with cannabis roots, helping plants absorb more water and nutrients while providing the fungi with carbohydrates produced by the plant through photosynthesis.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the primary nutrients required by cannabis plants in larger quantities: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These are critical for plant growth, root development, and flower production.
Mulch
Mulch is a layer of material applied to the surface of soil to conserve moisture, improve fertility, and reduce weed growth. In cannabis cultivation, organic mulches like straw or leaves can also add nutrients to the soil as they decompose.
Mainlining
Mainlining is a cannabis training technique that involves creating a "manifold" by pruning and training the plant to form a hub off the main stem from which symmetrical branches grow. This can lead to an even canopy and larger yields.
Marijuana
Although less scientifically precise and often considered pejorative, "marijuana" is a common colloquial term for cannabis, particularly in reference to its use as a psychoactive drug.
Medium
The medium in cannabis cultivation refers to the substance in which plants grow. This can be soil, a soilless mix, or a hydroponic setup where roots grow directly in nutrient-rich water.

Mold
Mold is a type of fungus that can develop on cannabis plants, especially in conditions of high humidity and poor air circulation. Common types affecting cannabis include botrytis (bud rot) and powdery mildew, both of which can devastate crops if not controlled.
Manicuring
Manicuring is the process of trimming away the excess leaves from cannabis buds after harvest. This improves the bud's appearance and can also enhance the quality by reducing harshness when consumed.
N
- Node
- Nutrients
- Necrosis
- Nitrogen
- NFT (Nutrient Film Technique)
- Neem Oil
- Nug
- N-P-K Ratio
- Netting
- Non-Polar Solvent
Node
The node is the part of a plant stem where leaves and branches emerge. In cannabis cultivation, paying attention to node spacing can give insights into plant health and the efficiency of light use.
Nutrients
Nutrients are the minerals and compounds that plants need to grow, which in cannabis cultivation are often added to the water in hydroponic systems or to the soil. There are both macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
Necrosis
Necrosis refers to the death of cells or tissues in a plant, often seen as browning or dying off of leaves or stems. In cannabis, necrosis can be caused by nutrient deficiencies, pathogens, or environmental stress.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a macronutrient essential for plant growth, a key component of chlorophyll, and vital for protein synthesis. In cannabis, nitrogen is especially important during the vegetative stage for promoting healthy foliage growth.
NFT (Nutrient Film Technique)
The Nutrient Film Technique is a type of hydroponic system where a shallow stream of nutrient-rich water flows over the roots of plants, which are suspended in a channel, allowing for efficient nutrient absorption and aeration.
Neem Oil
Neem oil is an organic pesticide derived from the seeds of the neem tree, commonly used in cannabis cultivation to control pests like mites and aphids. It’s favored for being effective while also being safe for beneficial insects and humans when used properly.
Nug
A nug is a term used to describe a dense, well-formed cannabis flower, often considered high-quality and desirable due to its appearance and concentration of cannabinoids and terpenes.
N-P-K Ratio
The N-P-K ratio on fertilizers indicates the proportion of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) they contain. This ratio is important in cannabis cultivation for providing the right nutrients at the right stages of growth.
Netting
Netting in cannabis cultivation refers to the use of trellis or support nets to manage and support plant growth. It’s often used in the Screen of Green (SCROG) method to create an even canopy for better light distribution.
Non-Polar Solvent
Non-polar solvents like butane or propane are used in the extraction process to isolate cannabinoids and terpenes from plant material. These solvents dissolve the desirable oily compounds but not the polar water-soluble substances.
O
- Organic
- Overwatering
- Oxidation
- Osmosis
- Odor Control
- Open Pollination
- Outcross
- OG
- Ounce
- Offset
Organic
Organic cannabis cultivation involves using only natural substances and techniques for growing cannabis. This means avoiding synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms, instead relying on organic soil, compost, and natural pest control methods.
Overwatering
Overwatering occurs when cannabis plants receive more water than they can use or evaporate, leading to oxygen deprivation in the roots, potential nutrient uptake issues, and increased susceptibility to root diseases like root rot.
Oxidation
Oxidation in cannabis can refer to the degradation of cannabinoids and terpenes when exposed to oxygen, heat, and light. This process can affect the potency and flavor profile of cannabis, emphasizing the need for proper storage and curing methods.
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. In cannabis cultivation, osmosis is how water and nutrients are absorbed through the roots.
Odor Control
Odor control is an important consideration in cannabis cultivation to manage the strong, distinctive smell produced by the plants. Methods include carbon filters, ozone generators, and maintaining negative air pressure in grow rooms.
Open Pollination
Open pollination occurs when cannabis plants are naturally pollinated by wind, insects, or other natural mechanisms, as opposed to controlled or selective pollination by humans. It can lead to greater genetic diversity but less control over the offspring's characteristics.
Outcross
Outcross is the practice of breeding a cannabis plant with another unrelated plant to introduce new genetic traits, improve vigor, or increase genetic diversity. This is often done to enhance certain characteristics or to create new hybrid strains.
OG
OG is a term commonly used in strain names to denote a high-quality, potent lineage of cannabis, often with a reputation for strong effects. It is sometimes said to stand for "Ocean Grown," "Original Gangster," or simply “Original."
Ounce
An ounce is a unit of weight commonly used in the cannabis industry to measure amounts of cannabis flower. One ounce is equivalent to approximately 28 grams.
Offset
In the context of cannabis, offset can refer to a side shoot or a "sucker" that grows from the base or the nodes of the main stems. These can be left to grow or removed to direct more energy to the primary colas.
P
- Photosynthesis
- pH Level
- Photoperiod
- Propagation
- Pistil
- Pest Management
- Perlite
- Potassium (K)
- Pollen
- Phenotype
- Phosphorus (P)
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, including cannabis, use sunlight to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water, producing oxygen as a byproduct. This process is fundamental to plant growth and is a key factor in determining the health and yield of cannabis plants.
pH Level
pH level is a measure of how acidic or basic the water or soil is on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Cannabis plants typically prefer a slightly acidic pH for optimal nutrient uptake. Soil pH should be between 6.0 and 7.0, while hydroponic systems should be between 5.5 and 6.5.
Photoperiod
Photoperiod refers to the hours of light and darkness a cannabis plant receives. Cannabis plants are photoperiod-dependent, meaning they require specific light schedules to vegetate and flower properly. Typically, the vegetative phase is under 18 hours of light, while the flowering phase is initiated by 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness.
Propagation
Propagation in cannabis cultivation is the process of creating new plants from seeds or clones (cuttings from mature plants). It is a crucial skill for growers looking to expand their garden or maintain a steady cycle of plant production.
Pistil
Pistils are the reproductive parts of female cannabis flowers. They start as small white hairs that turn orange, red, or brown as the plant matures. Pistils can indicate the plant’s readiness for harvest; when many pistils darken and curl, it may be time to harvest.
Pest Management
Pest management in cannabis cultivation involves preventing, identifying, and controlling pests that can damage cannabis plants. This includes using natural predators, organic pesticides, and maintaining a clean and controlled growing environment.
Perlite
Perlite is a volcanic glass that is heated and expanded to create a lightweight, porous material used to aerate soil and improve drainage in cannabis cultivation.
Potassium (K)
Potassium is a macronutrient that is vital for cannabis plant health. It aids in water uptake, enzyme activation, and the synthesis of proteins and starches. Potassium is also critical during the flowering phase to produce healthy and potent buds.
Pollen
Pollen is the fine, powdery substance produced by the male cannabis plant's flowers. It contains the male plant's genetic material and can fertilize female plants, leading to seed production.
Phenotype
Phenotype refers to the observable characteristics and traits of a cannabis plant, such as height, leaf shape, color, and bud structure, which result from the interaction between the plant’s genetic makeup (genotype) and its environment.
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus is a vital macronutrient for cannabis plants, playing a key role in energy transfer, photosynthesis, and nutrient uptake. It's crucial for root development, flowering, and seed production, ensuring plants reach their full potential. Phosphorus deficiency can lead to stunted growth and delayed maturation.
Q
- Quarter
- Querkle
- Quick-Drying
- Quantum Board LED Grow Lights
- Quality Control
- Quartz
- QP
- Quercetin
- Quick Cure
Quarter
A quarter refers to a quarter-ounce of cannabis flower, a standard unit of measurement used in the cannabis industry and among consumers. It weighs approximately 7 grams and is a popular purchase size, offering a balance between variety and volume for personal use.
Querkle
Querkle is a cannabis strain known for its distinctive purple coloration and a complex bouquet of aromas, often reminiscent of berries or grapes. It is a cross between Purple Urkle and Space Queen, and its effects are typically relaxing and sedative, making it a favorite for evening use.
Quick-Drying
Quick-drying refers to methods used to dry harvested cannabis quickly, as opposed to the slower, more traditional curing processes. Quick-drying can be achieved through various methods, such as using a dehydrator, oven, or microwave, but it's generally not recommended as it can adversely affect the taste and potency of the cannabis.
Quantum Board LED Grow Lights
Quantum boards are a type of LED grow light that features a dense array of light-emitting diodes on a flat surface or board. They provide even light distribution, full-spectrum light outputs, and are energy-efficient. Quantum boards are a popular choice among growers for their low heat generation and longevity.
Quality Control
In cannabis cultivation and production, quality control (QC) is a critical process that ensures the product meets legal, safety, and quality standards. QC protocols may include testing for cannabinoid profiles, terpene content, contaminants, moisture levels, and ensuring consistent product labeling. Rigorous QC is essential to maintain consumer trust and comply with regulatory requirements.
Quartz
Quartz, in the context of cannabis consumption, typically relates to quartz bangers or nails used in dab rigs. Quartz is favored for its durability and ability to quickly conduct high heat, making it ideal for vaporizing cannabis concentrates while preserving their flavors and aromas.
QP
A QP, or quarter pound, is a measurement of cannabis flower weight, equivalent to 4 ounces or about 113.4 grams. It is commonly used in bulk trading and by consumers who prefer purchasing larger quantities.
Quercetin
Quercetin is a plant-derived flavonoid present in cannabis and many other plants. It's recognized for its potential therapeutic properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects. In cannabis, quercetin may contribute to the entourage effect, potentially enhancing the therapeutic outcomes of cannabinoid consumption.
Quick Cure
Quick cure techniques are used to expedite the drying and curing process of cannabis. While traditional curing can take weeks, quick curing methods aim to shorten this to days or even hours. However, this speed can come at the cost of the final product's quality, potentially leading to harsher taste and diminished terpene profiles.
R
- Root Bound
- Rhizosphere
- Rosin
- Rockwool
- Resin
- Regeneration
- Ripening
- Root Pruning
- Re-vegging
Root Bound
A condition where a plant’s roots have filled the container and can no longer expand, leading to stunted growth and potentially affecting the plant’s health. Transplanting the cannabis plant to a larger container can remedy this.
Rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the microenvironment surrounding a plant's roots, where a complex interaction occurs between the roots, soil, and a myriad of microorganisms. This zone is critical for nutrient uptake and can be optimized through beneficial microbes and proper nutrient management.
Rosin
Rosin is a solventless cannabis concentrate made by applying heat and pressure to cannabis material to extract the resinous sap. This method is praised for preserving the full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes while avoiding the use of chemical solvents.
Rockwool
Rockwool is an inert growing medium made from spinning molten rock into fine fibers. It is commonly used in hydroponic systems for its excellent water retention and aeration properties, providing a stable substrate for cannabis roots.
Resin
Resin in cannabis refers to the sticky, trichome-rich substance produced by the plant, containing the majority of its cannabinoids and terpenes. It is the main source of potency in the cannabis flower and is often extracted for various cannabis concentrates.
Regeneration
Regeneration is a technique where a harvested cannabis plant is prompted to grow vegetatively again. By leaving some foliage on the plant and adjusting the light cycle back to vegetative conditions, the plant can produce a second, though usually smaller, harvest.
Ripening
Ripening is the final stage of a cannabis plant's flower development, where the plant's cannabinoids and terpenes reach their peak concentration. Proper observation of trichome maturity can help determine the best time to harvest.
Root Pruning
Root pruning involves trimming the roots of a cannabis plant to encourage the growth of new feeder roots, which can lead to improved nutrient and water uptake. This technique is often used in tandem with repotting to prevent plants from becoming root-bound.
Re-vegging
Re-vegging is a process of returning a cannabis plant to the vegetative stage after it has begun flowering. This is done by changing the light cycle back to long days and short nights. Re-vegging can be used to prolong the life of a particular plant or to produce more clones from a flowering mother plant.
S
- Strain
- Sativa
- Screen of Green (SCROG)
- Substrate
- Sinsemilla
- Stomata
- Supercropping
- SOG (Sea of Green)
- Solventless Extraction
- Stigma
- Sclerotinia
- Stress Training
Strain
A strain is a specific genetic variant of the cannabis plant. Strains are bred for certain characteristics like flavor, aroma, effects, and growth habits. Indica, sativa, and hybrid strains offer different experiences and medicinal benefits.
Sativa
Sativa refers to one of the primary species of cannabis, known for its energizing and uplifting effects. Sativa plants typically have longer flowering cycles and grow taller with narrower leaves compared to indica plants.
Screen of Green (SCROG)
SCROG is a training technique where plants are grown through a horizontal screen. This maximizes light exposure and air circulation, encourages even canopy development, and can lead to increased yields.
Substrate
The substrate is the base material in which plants root. In cannabis cultivation, substrates can range from soil to soilless mixes, such as coco coir or hydroponic media.
Sinsemilla
Sinsemilla, from the Spanish "sin semilla" meaning "without seed," refers to cannabis flowers that have not been fertilized by male pollen and therefore don't produce seeds. Sinsemilla buds are known for their higher concentration of cannabinoids.
Stomata
Stomata are tiny openings on the underside of cannabis leaves that allow for gas exchange. They play a critical role in photosynthesis and transpiration, helping to regulate the plant's water and CO2 intake.
Supercropping
Supercropping is a high-stress training technique where the stem of a cannabis plant is bent and lightly pinched, causing a knuckle to form. This can help control plant height and promote a bushier growth pattern.
SOG (Sea of Green)
Sea of Green is a growing method that involves planting many small cannabis plants close together to create a "sea" of green canopy. This method allows for quicker harvests and efficient use of space.
Solventless Extraction
Solventless extraction refers to methods of extracting cannabinoids and terpenes without using chemical solvents. Techniques include manual separation, dry sifting, water-based extraction (bubble hash), and heat and pressure (rosin).
Stigma
The stigma is part of the female cannabis plant's anatomy; they are the sticky hairs on the pistil where pollen lands to start the fertilization process. Stigmas are indicators of plant maturity and are typically white to start, turning orange, red, or brown as the plant gets closer to harvest.
Sclerotinia
Sclerotinia, also known as white mold or cottony rot, is a type of fungal disease that affects cannabis plants, causing wilt, stem rot, and bud rot, especially in high humidity environments.
Stress Training
Stress training refers to various techniques used to control plant growth and increase yield by carefully stressing the plants, including both low-stress training (LST) and high-stress training (HST) methods like topping, FIMing, and supercropping.
T
- Terpenes
- Topping
- Trichomes
- Transplanting
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
- Tincture
- Trellising
- Tillering
- Thermoperiodicity
- Trimming
Terpenes
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in cannabis and many other plants that contribute to their scent and flavor. In cannabis, terpenes can influence the effects of cannabinoids through the entourage effect and offer various therapeutic benefits.
Topping
Topping is a cannabis plant training technique that involves cutting off the top of the main stem to encourage lateral growth. This can lead to a bushier plant with more colas, potentially increasing the yield.
Trichomes
Trichomes are the small, crystal-like structures on the surface of cannabis flowers and leaves that produce and contain the plant's cannabinoids and terpenes. They give buds their frosty appearance and are a key indicator of potency and maturity.
Transplanting
Transplanting is the process of moving a cannabis plant from one container to a larger one to accommodate root growth. Proper transplanting can reduce the risk of becoming root-bound and encourage healthier, more robust growth.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis that produces the high associated with its use. It's one of many cannabinoids found in the plant and is subject to varying legal regulations worldwide.
Tincture
A tincture is a liquid cannabis extract made by dissolving cannabinoids into alcohol or another solvent. It's usually administered sublingually for fast absorption and precise dosing.
Trellising
Trellising involves using a grid-like support structure to train and manage the growth of cannabis plants. It helps spread the plant out for better light exposure and air circulation, which can lead to improved yield and health.
Tillering
Tillering refers to the growth of side shoots from the base of the plant or between the nodes. In cannabis, encouraging tiller growth can increase the number of potential flowering sites.
Thermoperiodicity
Thermoperiodicity is the plant's response to temperature fluctuations over a 24-hour period, which can affect growth and flowering cycles in cannabis.
Trimming
Trimming is the post-harvest process of removing the excess leaves from cannabis buds, which can be done wet (immediately after harvest) or dry (after curing). Proper trimming enhances the appearance and improves the smoking experience by reducing harshness.
U
- UV Light
- Uptake
- Undercutting
- Unisex
- Uniformity
- Up-Potting
- Urban Gardening
- Umbrella Training
- Undercutting
- Unisex
UV Light
Ultraviolet light, which includes UVA, UVB, and UVC rays, has varying effects on cannabis plants. UVA and UVB can stimulate THC production and improve plant resistance, while UVC is generally harmful. Grow lights that emit UV can be used to enhance the quality of cannabis.
Uptake
Uptake refers to a plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil or growth medium. Efficient uptake is vital for healthy growth and is influenced by factors such as pH levels, medium composition, and root health.
Undercutting
Undercutting is a horticultural technique where the lower parts of a plant are cut to encourage horizontal growth. This can be used in cannabis cultivation to control height and improve light exposure to lower branches.
Unisex
Unisex or monoecious refers to cannabis plants that have both male and female reproductive organs on the same plant. However, cannabis is typically dioecious, meaning individual plants are either male or female.
Uniformity
Uniformity in cannabis cultivation describes the consistency of plants in terms of size, shape, growth rate, and flowering time. High uniformity is often desired for ease of cultivation and can be achieved through stable genetics and consistent environmental conditions.
Up-Potting
Up-potting is the process of transplanting a cannabis plant into a larger pot to accommodate root growth and prevent becoming root-bound. This allows for continued growth and avoids stress that can slow down the plant's development.
Urban Gardening
Urban gardening refers to the practice of cultivating plants in an urban environment, which can include growing cannabis indoors or in small outdoor spaces like balconies or rooftops, using containers or small beds.
Umbrella Training
A plant training technique to shape cannabis plants into an umbrella-like form. This involves bending and tying the branches horizontally during the vegetative stage, which can increase light exposure and air circulation, leading to a more even canopy and potentially higher yields.
Undercutting
A method used to prune or trim the lower branches of a cannabis plant to focus the plant's energy on the top growth, encouraging a more bushy development and increasing airflow under the canopy.
Unisex
This term is used to describe plants that possess both male and female reproductive organs, allowing them to pollinate themselves. In cannabis, unisex plants are usually the result of stress and are not as common as separate male and female plants.
V
- Vegetative Stage
- Ventilation
- Vermiculite
- Vertical Growing
- Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD)
- Volatilization
- Viability
- Virus
- Vascular System
- Variegation
Vegetative Stage
The phase in a cannabis plant's life cycle when it's growing in size and stature but not yet producing flowers. During this stage, the plant requires longer periods of light, typically 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial in indoor cannabis cultivation to control temperature and humidity, provide a steady supply of CO2, and prevent the buildup of mold and mildew.
Vermiculite
A mineral used in cannabis cultivation as a soil amendment due to its ability to improve aeration and moisture retention in the growing medium.
Vertical Growing
A space-efficient growing technique where cannabis is cultivated in a vertical, stacked arrangement, allowing for more plants to be grown in a smaller footprint.
Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD)
VPD is a measure of the difference between the amount of moisture in the air and the amount of moisture the air can hold when it's saturated. It's an important concept for understanding how well plants can take up water and nutrients.
Volatilization
The process by which a substance changes from a liquid or solid state into a vapor. In cannabis, this can refer to the release of terpenes and cannabinoids at high temperatures.
Viability
In terms of cannabis seeds, viability refers to the seed's ability to germinate and develop into a healthy plant. High viability rates are desirable for growers to ensure successful cultivation.
Virus
Viruses can infect cannabis plants, leading to symptoms like stunted growth, leaf discoloration, and reduced yields. Good hygiene practices and plant management are necessary to prevent viral infections.
Vascular System
The network of xylem and phloem within a cannabis plant that transports water, nutrients, and sugars to various parts of the plant. A healthy vascular system is essential for robust plant growth.
Variegation
A condition where a plant's leaves have areas of different colors, usually due to genetic mutations, viruses, or nutrient deficiencies. While sometimes aesthetically pleasing, it can be a sign of an underlying issue with the plant.
W
- Watering Schedule
- Wattage
- Wicking
- Weeding
- Wet Trimming
- Windburn
- White Label
- Worm Castings
- Whole Plant Extract
- Wilting
Watering Schedule
The planned frequency and amount of water given to cannabis plants. An effective watering schedule takes into account the plant's growth stage, size, and the environment to prevent both underwatering and overwatering.
Wattage
Refers to the power consumption of electric devices, like grow lights. In cannabis cultivation, knowing the wattage of lights is important for managing energy costs and providing the proper amount of light intensity for plant growth.
Wicking
A method of hydroponic cultivation where a material, such as a rope or felt, draws nutrient-rich water from a reservoir to the plants' roots through capillary action.
Weeding
The process of removing unwanted plants (weeds) that compete with cannabis for nutrients, light, and space. Weeding helps to ensure that the cannabis plants can grow without competition and stress.
Wet Trimming
A harvesting technique where the excess leaves of a cannabis plant are trimmed away while the plant is still freshly harvested and wet. This is often done to streamline the drying process and to prevent mold.
Windburn
A condition where plants exhibit signs of stress, such as curled or clawing leaves, due to excessive wind or a strong fan in an indoor grow area. Proper ventilation without direct, forceful air on the plants can prevent windburn.
White Label
Products produced by one company that are packaged and sold under another company's brand name. In cannabis, white labeling is common for edibles, concentrates, and other products.
Worm Castings
The nutrient-rich waste produced by earthworms. Worm castings are an excellent organic fertilizer for cannabis, providing a good balance of nutrients, and can improve soil structure and microbial life.
Whole Plant Extract
A type of cannabis extract where the entire plant is used in the extraction process, preserving the full spectrum of cannabinoids, terpenes, and other beneficial compounds.
Wilting
A sign of stress in cannabis plants, often due to inadequate water intake, where leaves droop and may turn yellow. Wilting can also be caused by root problems, overwatering, or diseases.
X
- Xanthophyll
- Xeriscaping
- Xylem
- Xerophyte
- X-Factor
Xanthophyll
Xanthophylls are yellow pigments that belong to the class of carotenoids in plants. In cannabis, these pigments can contribute to the coloration of leaves, especially in the fall when chlorophyll breaks down and allows the xanthophylls to become more visible.
Xeriscaping
Xeriscaping refers to a landscaping method designed for areas that are susceptible to drought or where water conservation is practiced. While cannabis typically requires a good amount of water, some principles of xeriscaping can be applied to reduce water usage without stressing the plants, like mulching and using drought-resistant plant varieties.
Xylem
Xylem is a type of plant tissue that transports water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and flowers. In cannabis cultivation, maintaining healthy xylem is critical because it supports the plant’s growth by ensuring that all parts receive the necessary hydration and nutrition.
Xerophyte
A xerophyte is a plant adapted to grow in conditions with very low water availability. Cannabis isn't naturally a xerophyte, but understanding the traits of these plants can offer insights into breeding or cultivating cannabis in arid conditions.
X-Factor
The "X-Factor" in cannabis cultivation could refer to a variable in the growing environment or genetic makeup that has a significant but potentially unquantifiable impact on the quality or characteristics of the final product.
Y
- Yellowing
- Yield
- Yucca
- Yumbolt
Yellowing
This term refers to the yellowing of leaves, which can be a symptom of various issues, including nutrient deficiencies, overwatering, or a pH imbalance. Addressing the underlying cause is crucial to restoring plant health.
Yield
The amount of cannabis produced by a plant or crop. Yield can be influenced by genetics, growing conditions, cultivation techniques, and the skill of the grower. Optimizing yield is often a key objective in cannabis cultivation.
Yucca
Yucca extract is sometimes used in cannabis cultivation as a natural wetting agent to help with water penetration in soils, improving water uptake by the plant's roots.
Yumbolt
A cannabis strain known for its sedative effects, often sought after for its potential to alleviate insomnia and stress. Strains like Yumbolt are highlighted for their unique properties and genetic lineage.
Z
- Zeolite
- Zinc (Zn)
- Zonal Germination
- Zymurgy
Zeolite
A mineral that's sometimes added to cannabis grow mediums to improve water retention and nutrient exchange. Zeolite can also help with ion-exchange and as a soil conditioner in cannabis cultivation.
Zinc (Zn)
An essential micronutrient for plant growth, zinc plays a key role in chlorophyll production, growth hormone synthesis, and enzyme systems. Zinc deficiencies can lead to stunted growth and distorted leaves.
Zonal Germination
This term isn't commonly used in cannabis cultivation, but it could refer to the practice of germinating seeds based on specific climate zones to ensure optimal growth conditions.
Zymurgy
The study of fermentation, which is tangentially related to cannabis through the fermentation of raw cannabis to produce certain types of extracts or the use of fermented plant extracts as organic fertilizers.